Two electric charges, which are not in contact, can exert electrical forces on each other. The concept of electric field is used to explain this phenomenon.
ထိစပ္ေနျခင္းမရွိေသာ္လည္း လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ႏွစ္ခုၾကားတြင္ တစ္ခုကိုတစ္ခု လွ်ပ္စစ္အားမ်ားသက္ေရာက္ေစႏိုင္ပါသည္။ ဒီျဖစ္စဥ္ကို ရွင္းလင္းတင္ျပရန္အတြက္ လွ်ပ္စစ္စက္ကြင္း၏အေဘာတရားမ်ားကို အသံုးျပဳခဲ့ပါသည္။
COULOMB'S LAW
Just as there is a gravitational force between two masses so there is an electric force between two charged particles. Electrical forces bind electrons and nuclei to form atoms. In addition, these forces hold atoms to form molecules, liquids and solids. It has already been mentioned in mechanics that there are only four fundamental forces, namely, gravitational force, weak interaction, electromagnetic force and nuclear force. Of these forces gravitational and electromagnetic forces are long-range forces.
အရာ၀တၳဳႏွစ္ခုၾကားတြင္ ကမၻာေျမဆဲြအားသက္ေရာက္ေနသကဲ့သို႔ လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ေဆာင္အမႈန္ႏွစ္ခုၾကားတြင္လည္း electric force (လွ်ပ္စစ္သက္ေရာက္အား) တစ္ခုသက္ေရာက္ေနပါသည္။ ၎ electric forces မ်ားသည္ atom အမႈန္တစ္ခုျဖစ္လာရန္ electrons မ်ားႏွင့္ nuclei မ်ားကို မကဲြကြာေအာင္တြဲေႏွာင္ထားပါသည္။ ထိုျပင္ ၎ electric forces မ်ားသည္ molecules မ်ား၊ အရည္မ်ား၊ အစိုင္အခဲမ်ားျဖစ္လာေအာင္ atom မ်ားကို ေပါင္းစည္းေစသည္။ အမည္အားျဖင့္ gravitational force (ကမၻာ႕ေျမဆြဲအား)၊ weak interaction (သတၱိၾကြအား)၊ electromagnetic force (လွ်ပ္စစ္သံလိုက္စက္ကြင္းအား)၊ nuclear force (နယူကလိယားအႏုျမဴအား) ဟူ၍ အေျခခံအားေလးမ်ဳိးရွိသည္ကို mechanics သင္ခန္းစာအခန္းမ်ားတြင္တင္ျပေပးခဲျပီးျဖစ္သည္။ ထိုအားေလးမ်ဳိးတြင္ gravitational force ႏွင့္ electromagnetic force ႏွစ္ခုသည္ တာေ၀သို႔တိုင္ေအာင္သက္ေရာက္ေစႏိုင္ေသာေၾကာင့္ ၎အားႏွစ္မ်ဳိးကို long-range forces မ်ားဟုေခၚသည္။
The French scientist, Coulomb, studied systematically the attractive and repulsive forces acting between pairs of charges and discovered a certain law. This law is called Coulomb's law and it states that:
The electric force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to square of the distance between them.
ျပင္သစ္သိပၸံပညာရွင္ျဖစ္ေသာ Coulomb ဆိုသူသည္ လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ႏွစ္ခုၾကားတြင္ သက္ေရာက္ေနေသာ ဆဲြအားႏွင့္တြန္းအားမ်ားကို နည္းစနစ္က်က်ေလ့လာခဲ့ျပီး၊ သိက်ေသခ်ာေသာနိယာမတစ္ခုကိုရွာေဖြေဖာ္ထုတ္ခဲ့သည္။ ၎နိယာမကို Coulomb's Law ဟုေခၚဆိုျပီး ေဖာ္ျပခ်က္မွာေအာက္ပါအတိိုင္းျဖစ္သည္။
လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ႏွစ္ခုၾကားတြင္ သက္ေရာက္ေနေသာသက္ေရာက္အားသည္ ၎လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ပမာဏမ်ားေျမာက္လဒ္ျဖင့္ တိုက္ရိုက္အခ်ဳိးက်ျပီး၊ ၎လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ႏွစ္ခု၏အကြာေ၀းႏွင့္ေျပာင္းျပန္အခ်ိဳးက်သည္။ ဆိုလိုသည္မွာ Chargeႏွစ္ခု ပမာဏမ်ားလာလွ်င္ Force မ်ားလာျပီး၊ Charge ႏွစ္ခုပိုေ၀းေလေလ Force သည္လည္း နည္းလာေလေလျဖစ္သည္။
အထက္ပါပံုတြင္ q₁ ႏွင့္ q₂ တို႔သည္ electric charges မ်ားျဖစ္ျပီး r သည္ ၎ charges ႏွစ္ခုၾကားအကြားအေ၀းျဖစ္ေသာ္ သခ်ာၤနည္းျဖင့္ Coulomb's law ကို ေအာက္ပါအတိုင္းတင္ျပႏိုင္သည္။
Since the force F is inversely proportional to r², Coulomb's law is also called an inverse square law.
သက္ေရာက္အား F သည္ အကြာအေ၀း r ႏွစ္ထပ္ကိန္းႏွင့္ ေျပာင္းျပန္အခ်ိဳးက်ေနေသာေၾကာင့္ Coulomb's law ကို ႏွစ္ထပ္ကိန္းေျပာင္းျပန္နိယာမ inverse square law ဟုလည္းထပ္မံေခၚဆုိပါသည္။
In equation, K is a constant. The value of K depends upon the units of F, q₁, q₂ and r and upon the medium in which the charge q₁ and q₂ are located.
အထက္ပါ equation တြင္ K တန္ဖိုးသည္ ကိန္းေသျဖစ္သည္။ K ၏တန္ဖိုးသည္ F, q₁, q₂, r တို႔ႏွင့္ q₁, q₂ တို႔တည္ရွိေသာၾကားခံအရာ၀တၳဳ (ၾကားခံနယ္) အေပၚတြင္သာ မီွတည္ေျပာင္းလဲပါလိမ္မည္။
Electrical force is, of course, a vector quantity. Equation only gives the magnitude of the force between two electric charges. The direction of electrical force is always along the ling joining the two charges. If the charges are like charges the force between them is repulsive and is directed outward. If the charges is unlike charges the force between them is attractive and directed inward.
အမွန္တကယ္တြင္ electrical force သည္ vector quantity သာျဖစ္သည္။ အထက္ပါ equation သည္ လွ်ပ္စစ္ဓါတ္ႏွစ္ခုၾကားတြင္ျဖစ္ေပၚေနေသာ force ၏ပမာဏတန္ဖိုးကိုသာေဖၚျပေပးပါသည္။ electrical force ၏ ဦးတည္ဘက္သြားရာသည္ ၎ charges ႏွစ္ခုကိုဆက္သြယ္ထားေသာ မ်ဥ္းေၾကာင္းလႈိင္းအတိုင္းသာ ဦးတည္ေနၾကသည္။ Charges မ်ား အမ်ဳိးအစားတူေနလွ်င္ Force သည္ တြန္းကန္အားျဖစ္ၿပီး၊ ဦးတည္ဘက္သြားရာသည္ အျပင္သို႔ျဖစ္သည္။ Charges မ်ား အမ်ိဳးအစားမတူၾကလွ်င္ Force သည္ ဆဲြအားျဖစ္ျပီး၊ ဦးတည္ဘက္သြားရာသည္ အတြင္းသို႔ျဖစ္သည္ကို ေအာက္ပါပံုတြင္ၾကည့္ပါ။
In the SI system, charge q is measured in coulomb, the distance r in meter and the force F in newton. In The SI system,
SI စနစ္တြင္၊ Charge q ကို coulomb (C) unit ျဖင့္တိုင္းတားတြက္ခ်က္ၿပီး၊ အကြာအေ၀း r ကို meter (m) ျဖင့္လည္းေကာင္း the force F ကို newton (N) ယူနစ္တို႔ျဖင့္လည္းေကာင္း တိုင္းတာတြက္ခ်က္ၾကသည္။ SI စနစ္တြင္ K တန္ဖုိး equation မွာ
Where 𝞮 is a constant called the permittivity of the medium in which the charges are located. Then, equation can be rewritten as
𝞮 ကို charges မ်ားတည္ရွိေသာ ၾကားခံနယ္၏ျဖတ္သန္းႏႈန္းကိန္းေသျဖစ္ေနေစသာအခါ K တန္ဖိုး equation မွာ
Where charges are located in Vacuum,
Charges မ်ား ေလဟာနယ္ (Vacuum) အတြင္းတည္ရွိေနေသာအခါ
Therefore,
where Ɛ₀ is the permittivity of vacuum and
Ɛ₀ ကို ေလဟာနယ္ျဖတ္သန္းႏႈန္းမွတ္ယူေသာအခါ Ɛ₀ ၏ တန္ဖိုးမွာ
and the value of K in vacuum is
ထိုေၾကာင့္ ေလဟာနယ္ထဲတြင္ရွိေသာ K ၏တန္ဖိုးမွာ
However, for convenience in calculation, the value of K in vacuum will be taken as
သို႔ေသာ္လည္း အျပည္ျပည္ဆိုင္ရာသြက္ခ်က္မႈမ်ားတြင္ ေလဟာနယ္တြင္းရွိ K ၏တန္ဖိုးကို ေအာက္ပါအတိုင္းတြက္ယူၾကသည္။
The value of K in air is approximately equal to that of K in vacuum.
ေလထဲတြင္ရွိေသာ K ၏ တန္ဖိုးႏွင့္ ေလဟာနယ္ထဲတြင္ရွိေသာ K ၏တန္ဖိုးတို႔သည္ ထပ္တူနီးပါ တန္ဖိုးညီေနၾကသည္။







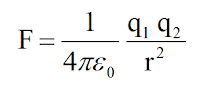













0 comments:
Post a Comment